The creation of phased SNP genotype data is done in 5 steps as follows.
Step 1.
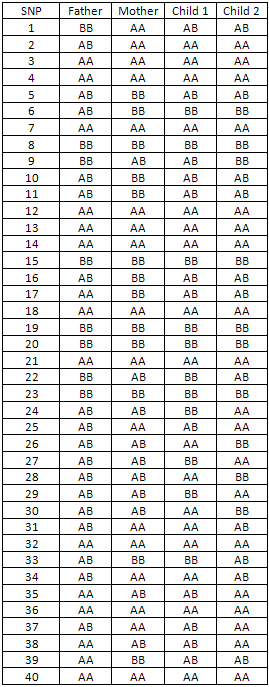
Table 1
The SNP data is ordered by chromosome and position (Table 1).
Step 2.
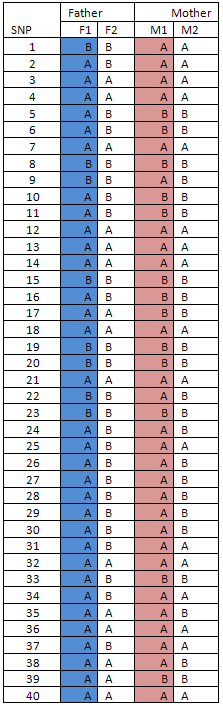
Table 2
For each parent, the genotyping data from the two individual chromosomes that form the the pair of autosome homologues are allocated into separate data sets. Each of the two data sets is used to represent an individual chromosome. When a SNP is heterozygous, the first chromosome of the homologue pair ('F1' and 'M1') is allocated the A major allele (table 2). In the tables below, each extended haplotype is coloured blue for the first paternal chromosome ('F1') and pink for the first maternal chromosome ('M1').
Step 3.
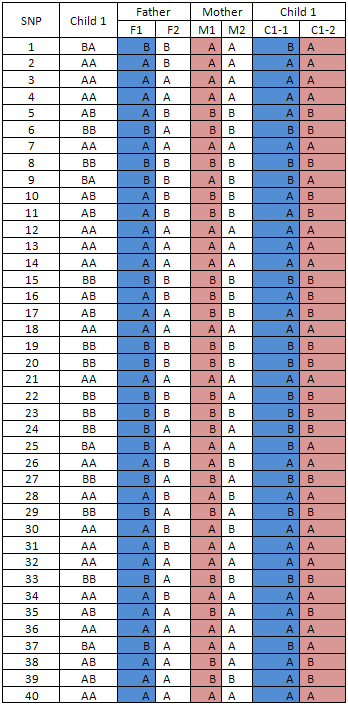
Table 3
The alleles for each individual paternal chromosome are then compared to the genotypes for the first child (C1) in the family. The order of the child's alleles (i.e. on the first or second chromosome of the homologue, 'C1-1' or 'C1-2') is adjusted to ensure that the 'F1' and 'M1' haplotypes are inherited in their entirety by the first child in the family. The parental origin of each allele in the child is therefore arbitrary allocated on the basis of mendelian inheritance (table 3).
Step 4.
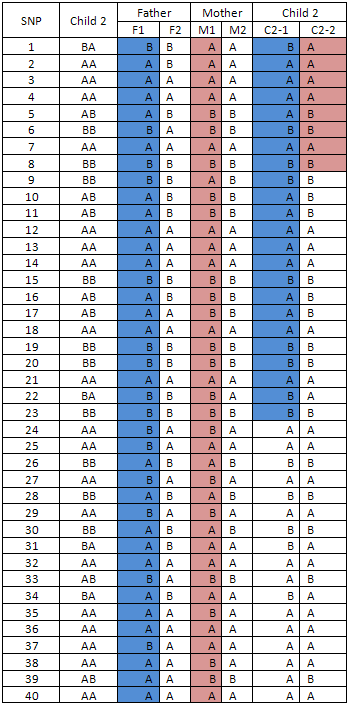
Table 4
The SNP genotypes of other children in the family (for example, a sibling C2) are then compared to the alleles for each of the parental 'F1' and 'M1' haplotypes. Haplotypes that match those of the first child ('C1-1' and 'C1-2') are coloured blue or pink according to their parental origin. Alleles that cannot be inferred to have been transmitted from the 'F1' and 'M1' parental haplotypes must therefore have arisen from the second chromosome of the homologue ('F2' and 'M2') due to recombination and are left uncoloured (table 4).
Step 5.
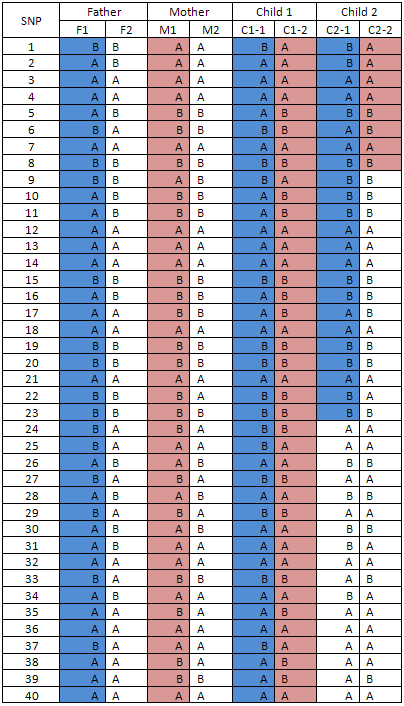
Table 5
The parental origin of the alleles on each individual's chromosomes is used to determine the origin and extent of any common or shared haplotype between individuals in the complete nuclear family. In Table 5, a maternal region is shared by Child 1 and Child 2 between SNP1 and SNP8 and a paternal region is shared by them between SNP1 and SNP23.